Qakbot Being Distributed as ISO Files Instead of Excel Macro

There is a recent increase in the distribution method of malware through ISO files. Among the malware, it has been identified that Qakbot, an online banking malware, has had its distribution method changed from Excel 4.0 Macro to ISO files. The ASEC blog introduced cases of ISO file usage for not only Qakbot, but also AsyncRAT, IcedID, and BumbleBee malware. As such, we can see that cases of using ISO files for malware distribution are increasing.
The phishing mail that distributes Qakbot is shown in Figure 1, and a malicious HTML file is attached to it.

When the attached HTML file is executed, the page shown in Figure 2 opens, and the compressed file within the script is created. The compressed file is password-protected, and the password can be found on the HTML page.
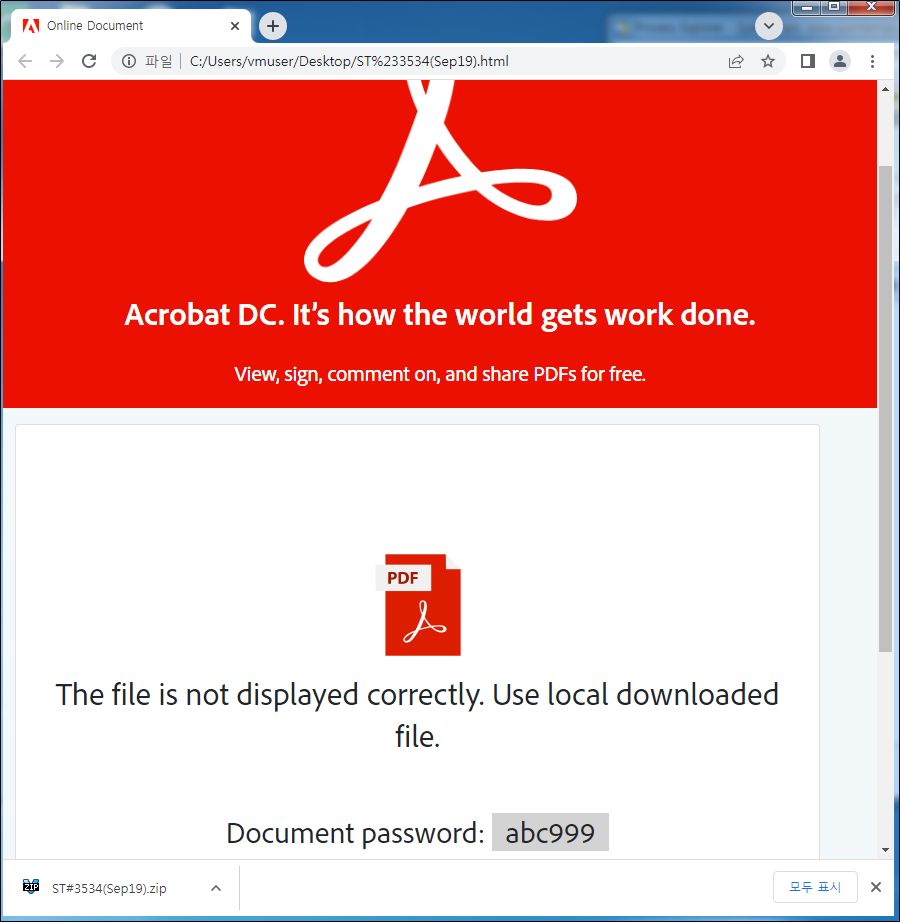
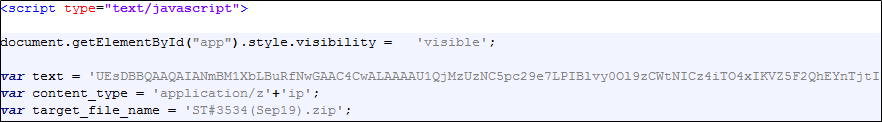
There is an ISO file inside the compressed file, and the ISO file contains an LNK file and a folder. This folder contains multiple files, including both normal and malicious files (See Figure 6).


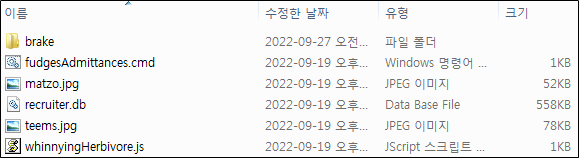
The LNK file is disguised as a folder icon, and executing this will launch the malicious JS file inside the “conspicuously” folder.

The malicious JS file serves the role of executing the cmd file in the same folder with the argument “regsvr”. The cmd file combines the strings “regsvr” and “32” transmitted with the argument and ultimately loads the recruiter.db file through regsvr32.exe. The file loaded at this point is Qakbot, the banking malware.


The Qakbot malware first checks to see if the “C:\INTERNAL\__empty” path file exists, and if it does exist, the malware does not perform malicious behaviors. This is assumed to be the process of scanning the emulation string of Windows Defender.

It also checks whether the PC is infected or not via environmental variables, and when a particular environmental variable does not exist, it performs malicious behaviors. Afterward, it steals the username, information on currently running processes, OS information, etc., then performs an injection to normal processes. The target processes for injection are as follows.
- Normal processes targeted for injection
C:\Windows\explorer.exe
C:\Windows\System32\msra.exe
C:\Windows\System32\OneDriveSetup.exe
The injected processes decode multiple C2s to attempt a connection, and a portion of these are shown below. When a connection to C2 is made, additional malicious behaviors can be performed, including downloading malicious modules and stealing financial information.
- C2
154.181.203[.]230:995
66.181.164[.]43:443
197.204.143[.]46:443
37.76.197[.]124:443
89.211.223[.]138:2222
151.234.63[.]48:990
31.54.39[.]153:2078
61.105.45[.]244:443
186.105.182[.]127:443
181.231.229[.]133:443
62.114.193[.]186:995
70.81.121[.]237:2222
1.10.253[.]207:443
138.0.114[.]166:443
102.101.231[.]141:443
177.255.14[.]99:995
203.77.187[.]131:80
Recently, there has been an increase in malware distribution using ISO files, and users must refrain from opening attachments within emails. AhnLab’s anti-malware product, V3, detects and blocks the malware using the alias below.
[File Detection]
Malware/Win.Generic.C5240833 (2022.09.21.00)
Dropper/HTML.Qakbot (2022.09.30.03)
Trojan/CMD.Runner (2022.09.30.03)
Trojan/JS.Runner (2022.09.30.03)





